Iron-Catalyzed Skeletal Conversion of Lathyrane to Premyrsinane Euphorbia Diterpenes and
Their Cytotoxic Activities
Yao Xiao1, Neng Wang1, Lin-Xi Wan1, Xian-Li Zhou1*, Xiaohuan Li1*, Feng Gao1*
1. School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
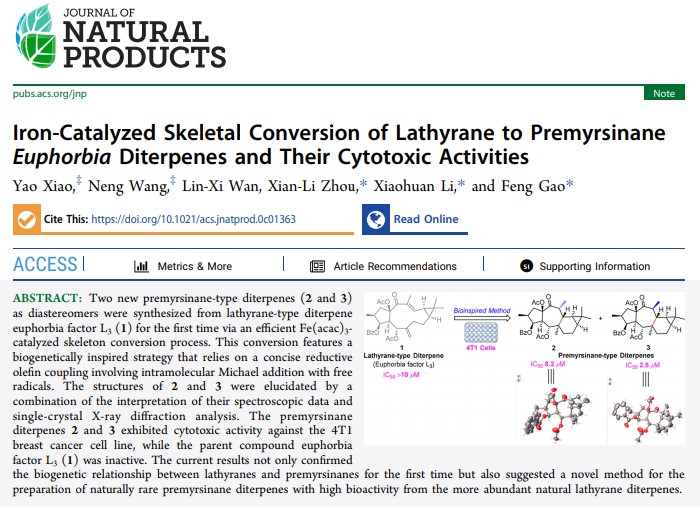
Two new premyrsinane-type diterpenes (2 and 3) as diastereomers were synthesized from lathyrane-type diterpene euphorbia factor L3 (1) for the first time via an efficient Fe(acac)3-catalyzed skeleton conversion process. This conversion features a biogenetically inspired strategy that relies on a concise reductive olefin coupling involving intramolecular Michael addition with free radicals. The structures of 2 and 3 were elucidated by a combination of the interpretation of their spectroscopic data and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The premyrsinane diterpenes 2 and 3 exhibited cytotoxic activity against the 4T1 breast cancer cell line, while the parent compound euphorbia factor L3 (1) was inactive. The current results not only confirmed the biogenetic relationship between lathyranes and premyrsinanes for the first time but also suggested a novel method for the preparation of naturally rare premyrsinane diterpenes with high bioactivity from the more abundant natural lathyrane diterpenes.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01363